What Are the First and Most Common Signs & Symptoms of Lung Cancer?
Lung cancer occurs when abnormal cells in the lungs grow uncontrollably, forming tumors that interfere with normal lung function. It is one of the most common and serious types of cancer, often diagnosed at an advanced stage due to a lack of noticeable early symptoms.
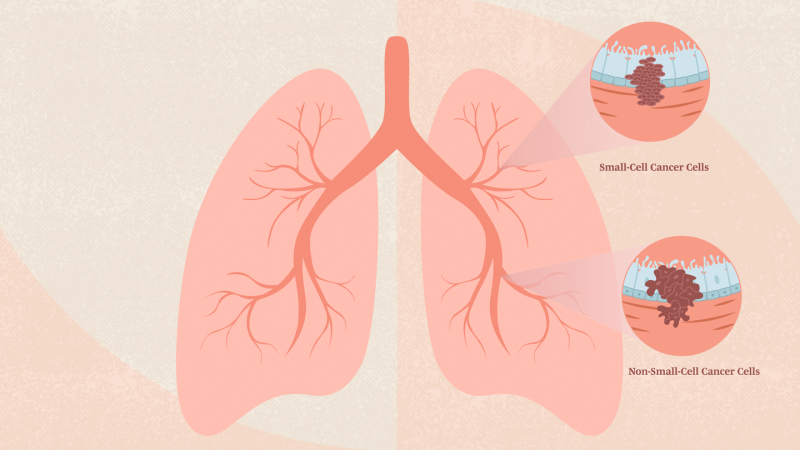
Types of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer is categorized into two main types:
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer (NSCLC) –
This is the most common type, accounting for about 85% of lung cancer cases. It generally progresses more slowly than small cell lung cancer.
Small Cell Lung Cancer (SCLC) –
Though less common, SCLC is more aggressive and spreads rapidly compared to NSCLC.
Early Signs and Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Some individuals may notice subtle changes in their health before more prominent symptoms appear. Recognizing these early signs can lead to timely diagnosis and treatment.
1. Persistent Cough
A cough that lasts more than a few weeks or worsens over time may be an early sign of lung cancer. Initially, it may be mild and occasional but can become more frequent and intense. If the cough is accompanied by blood (hemoptysis), chest pain, or shortness of breath, a doctor should be consulted immediately.
2. Chest Pain
Lung cancer can cause persistent chest pain that worsens with deep breathing, coughing, or laughing. The pain may be localized or spread to the shoulders, back, or upper abdomen. Tumors pressing on nerves, ribs, or chest structures can contribute to this discomfort.
3. Shortness of Breath
Difficulty breathing, even with minimal physical activity, could indicate a problem. Lung tumors can obstruct airways, causing breathlessness during routine activities such as walking or climbing stairs.
4. Coughing Up Blood (Hemoptysis)
Blood-streaked mucus or coughing up blood is a serious symptom that should not be ignored. While it can also be caused by infections or chronic bronchitis, hemoptysis requires immediate medical evaluation to rule out lung cancer.
5. Wheezing
A whistling or high-pitched sound when breathing can indicate narrowed or partially blocked airways. While wheezing is commonly associated with asthma or respiratory infections, its sudden onset without a history of such conditions should be investigated.
Other Symptoms to Be Aware Of
As lung cancer progresses, additional symptoms may develop, including:
1. Unexplained Fatigue
Extreme tiredness and weakness that persist despite rest can be a sign of lung cancer. The disease affects the body’s metabolism and can cause a constant feeling of exhaustion.
2. Unexplained Weight Loss
Losing weight without changes in diet or physical activity could indicate an underlying health issue. Cancer cells consume more energy, leading to weight loss and loss of appetite.
3. Hoarseness or Voice Changes
If lung tumors press on nerves controlling the voice box, it can lead to hoarseness or voice changes. If these changes persist for more than a few weeks, a doctor should be consulted.
4. Swelling in the Face or Neck
A tumor blocking blood flow in the superior vena cava, a major vein that returns blood to the heart, can cause swelling in the face, neck, or upper chest.
5. Headaches or Bone Pain
Lung cancer that has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bones or brain, can cause persistent headaches, bone pain (especially in the ribs or spine), and neurological symptoms like dizziness or weakness.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, especially a persistent cough, chest pain, or shortness of breath, it is essential to seek medical advice. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Preventive Measures and Risk Factors
While some risk factors, such as genetic predisposition, cannot be controlled, lifestyle changes can help reduce the risk of lung cancer:
Quit Smoking
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. Avoiding tobacco or quitting smoking greatly lowers the risk.
Avoid Secondhand Smoke
Exposure to tobacco smoke from others can also increase the risk.
Limit Exposure to Carcinogens
Workplace exposure to harmful substances like asbestos, radon, and industrial chemicals should be minimized.
Maintain a Healthy Diet
Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables supports lung health.
Exercise Regularly
Staying physically active boosts lung function and overall health.
Conclusion
Lung cancer often remains undetected until later stages, but being aware of early symptoms can lead to timely diagnosis and better treatment outcomes. Regular health check-ups and avoiding risk factors can help reduce the chances of developing lung cancer. If you or a loved one experiences persistent symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for proper evaluation and early intervention.
