What Is Stage 1, 2, 3, or 4 Cancer? Understanding the Staging System
Cancer staging describes the extent of cancer in your body. It plays a critical role in determining treatment options, predicting outcomes, and guiding ongoing care. Whether you’re newly diagnosed or supporting someone who is, understanding the stages of cancer helps clarify what the diagnosis means and what comes next.
In this guide, we will break down the staging process, including how oncologists determine cancer stage, what each stage (from 0 to 4) means, and how staging helps in personalized treatment planning.
What Is Cancer Staging?
Cancer staging is a way of describing how much cancer is in the body, where it is located, and how far it has spread. Doctors use staging to:
- Understand the severity of the cancer
- Plan the best treatment approach
- Estimate prognosis (likely outcome)
- Compare treatment results across patients
One of the most widely used staging tools is the TNM staging system developed by the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC).
How Cancer Is Staged: The TNM Staging System
The TNM system classifies cancer based on three key components:
- T (Tumor): Size and extent of the primary tumor
- N (Nodes): Whether cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes
- M (Metastasis): Whether cancer has spread to distant organs
Once the TNM values are assigned, doctors group them into numerical stages:
- Stage 0 (Carcinoma in situ)
- Stage 1 (Localized cancer)
- Stage 2 and 3 (Locally advanced cancer)
- Stage 4 (Metastatic cancer)
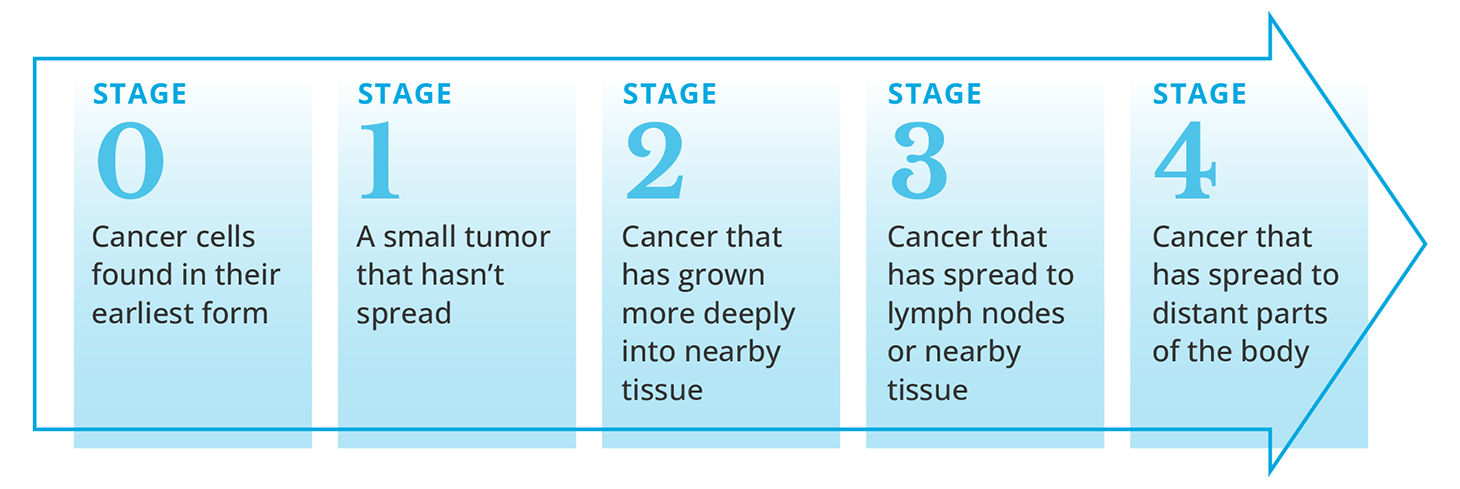
Cancer Stage Numbers Explained
Stage 0: Carcinoma in Situ
- Abnormal cells are present, but haven’t spread
- Often considered “pre-cancer”
- High potential for successful treatment
Stage 1: Localized Cancer
- Small tumor confined to one area
- No lymph node involvement
- Excellent prognosis
- Often treated with surgery or radiation therapy
Stage 2: Larger Tumor or Local Lymph Node Spread
- Tumor may have grown deeper into tissue
- May involve nearby lymph nodes
- Treatment may include surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation
Stage 3: Locally Advanced Cancer
- Cancer has spread more extensively in the region
- More lymph nodes may be involved
- Treatment is typically more aggressive (multi-modal)
Stage 4: Metastatic Cancer
- Cancer has spread to distant parts of the body
- Common sites include lungs, liver, brain, or bones
- Focus is often on managing symptoms and extending life (palliative care)
Clinical vs. Pathologic Staging
- Clinical staging is based on imaging tests and physical exams before surgery.
- Pathologic staging includes findings after surgery, such as biopsy or tumor removal.
Both are important and may differ slightly, influencing ongoing treatment.
Why Staging Matters in Cancer Treatment
Knowing the stage helps:
- Personalize treatment: Surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy
- Predict survival rates (prognosis)
- Monitor treatment response
- Guide enrollment in clinical trials
For example, Stage 1 breast cancer may only need surgery and hormone therapy, while Stage 4 colorectal cancer could involve targeted therapies and palliative care.
Voice Search Optimized FAQs
Q: What do the stages of cancer mean?
A: They describe how much the cancer has grown and whether it has spread.
Q: Is Stage 1 cancer serious?
A: It’s usually considered early-stage cancer with a good prognosis.
Q: What is the difference between stage and grade in cancer?
A: Stage refers to size and spread; grade refers to how abnormal the cancer cells look.
Q: Can Stage 4 cancer be cured?
A: It is usually not curable but may be managed to extend life and improve quality of life.
Q: How fast can cancer progress from stage 1 to 4?
A: It varies greatly depending on the type and biology of the cancer.
Q: What does TNM mean in cancer staging?
A: TNM stands for Tumor, Node, Metastasis — a system used to describe cancer’s spread.
Q: Does cancer staging affect treatment options?
A: Yes, treatment is planned based on the stage.
